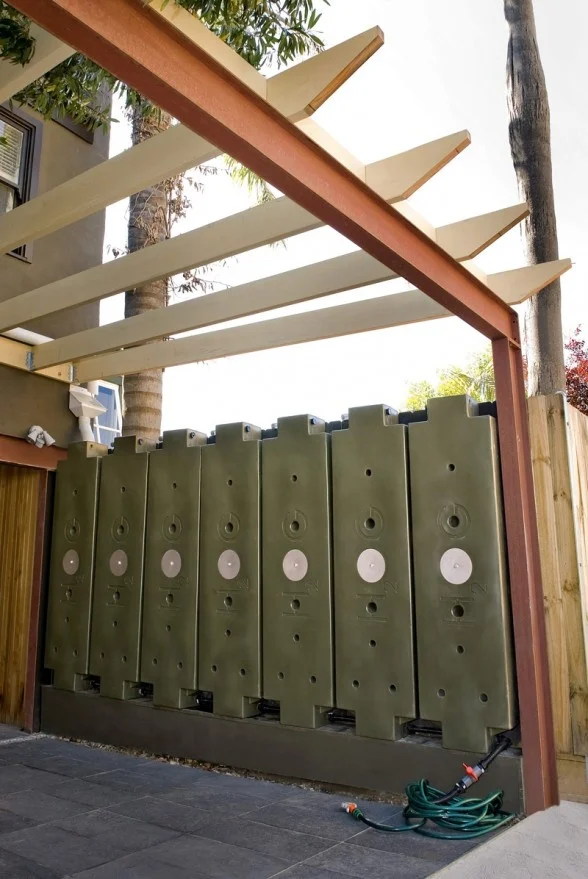
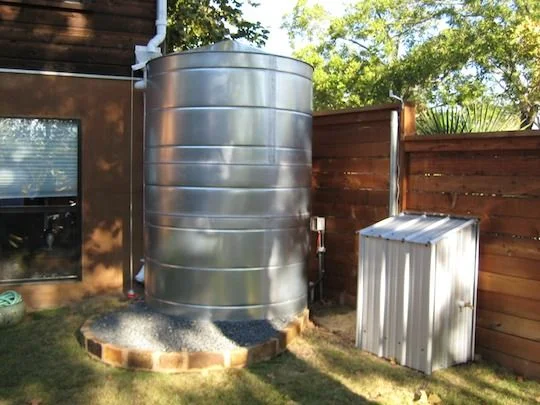
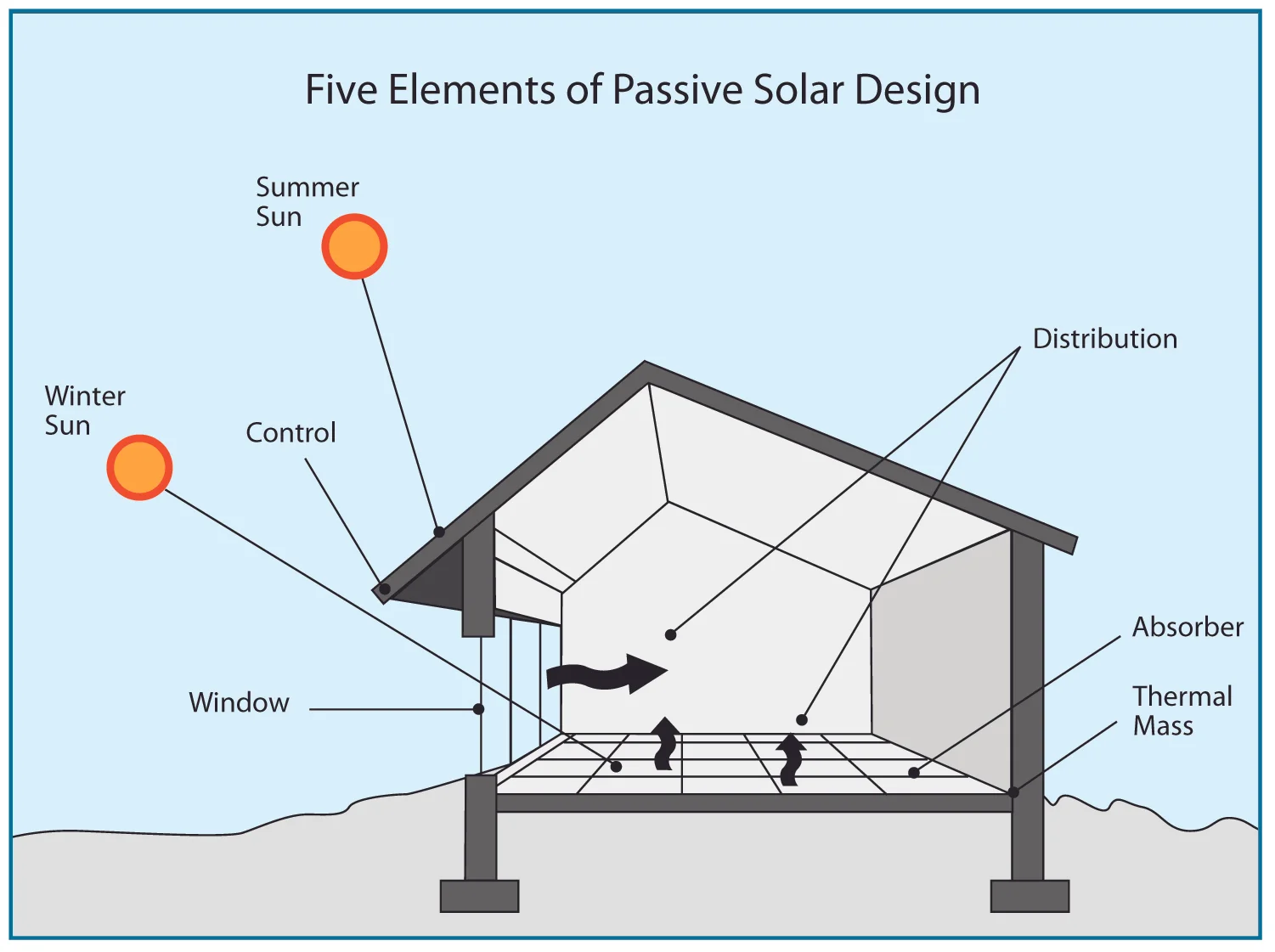
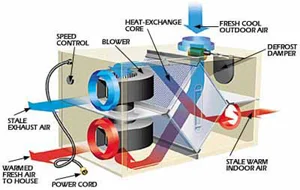
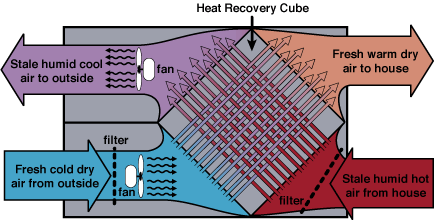
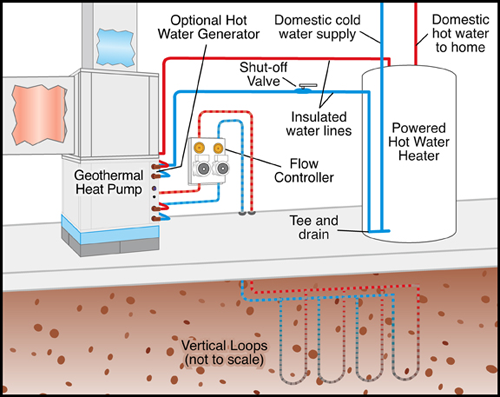
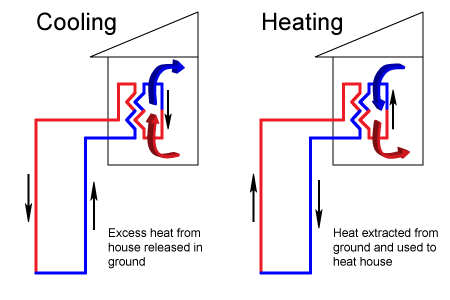
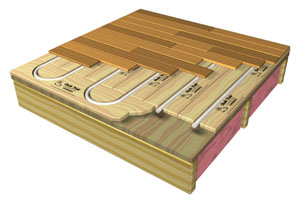
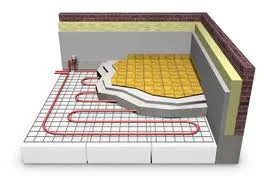
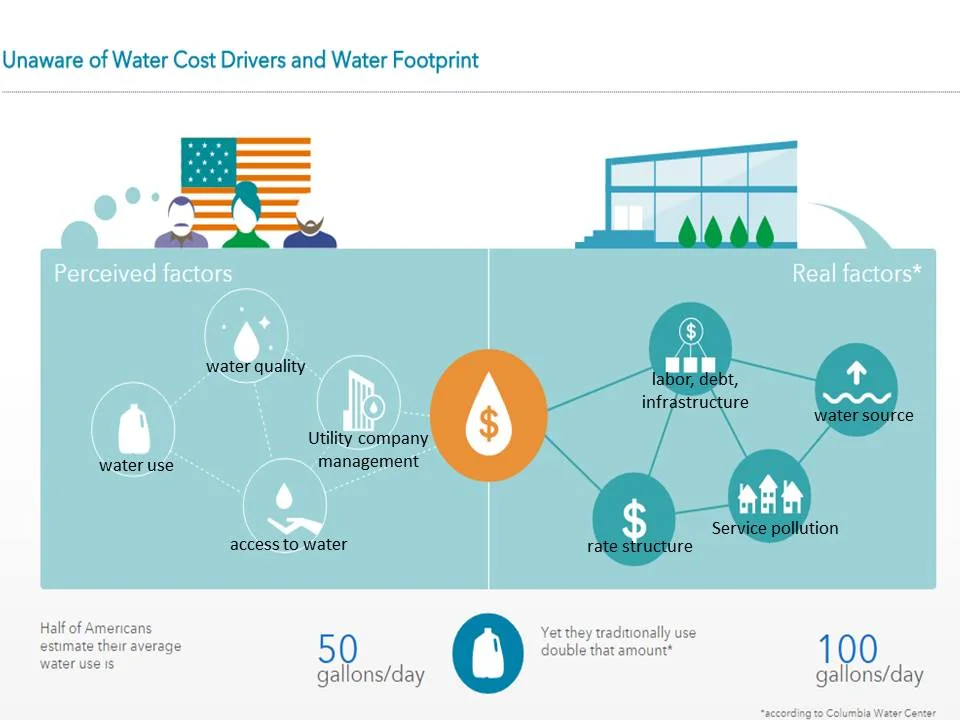
At KINDO Studios we believe that green design is responsible design and as such, it inherently informs every design decision. As designers that marry the built and natural environments we embrace our responsibility in shaping the discussion and the adoption of sustainable principles.
Rapidly rising energy costs
Escalating prices on consumer goods
Aging, unstable grid systems, Blackouts brownouts
Water shortages
Supply chain interruptions
More frequent economic losses due to increased storm intensity and flooding
zone depletion
Air & water pollution, Acid rain
Destruction of world’s forests and green spaces
Species & biodiversity loss
Collapse of world’s fisheries
Fresh water scarcity
Topsoil loss; soil contamination